1192 - Cleaning Robots
Tạo bởi: CLB Olympic Tin học HUTECH
Mô tả yêu cầu
The new ICPC town has N junctions (numbered from 1 to N) which are connected by N - 1 roads. It is possible from one junction to go to any other junctions by going through one or more roads. To make sure all the junctions are well-maintained, the government environment agency is planning to deploy their newest advanced cleaning robots. In addition to its cleaning ability, each robot is also equipped with a movement ability such that it can move from one junction to any other junctions connected by roads. However, as you might have guessed, such robots are not cheap. Therefore, the agency is considering the following deployment plan.
Let T_k be the set of junctions which should be cleaned by the k^{th} robot (also known as, the robot’s task), and |T_k| \geq 1 be the number of junctions in T_k. The junctions in T_k form a path, i.e. there exists a sequence of v_1, v_2, . . . ,v|T_k| where v_i \in T_k and v_i \neq v_j for all i \neq j such that each adjacent junction in this sequence is connected by a road. The union of T for all robots is equal to the set of all junctions in ICPC town. On the other hand, no two robots share a common junction, i.e. T_i \cap T_j = \varnothing if i \neq j.
To avoid complaints from citizens for an inefficient operation, the deployment plan should be irreducible; in other words, there should be no two robots, i and j, such that T_i \cup T_j forms a (longer) path. Note that the agency does not care whether the number of robots being used is minimized as long as all the tasks are irreducible.
Your task in this problem is to count the number of feasible deployment plan given the town’s layout. A plan is feasible if and only if it satisfies all the above-mentioned requirements.
For example, let N = 6 and the roads are {(1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6)}. There are 5 feasible deployment plans as shown in the following figure.
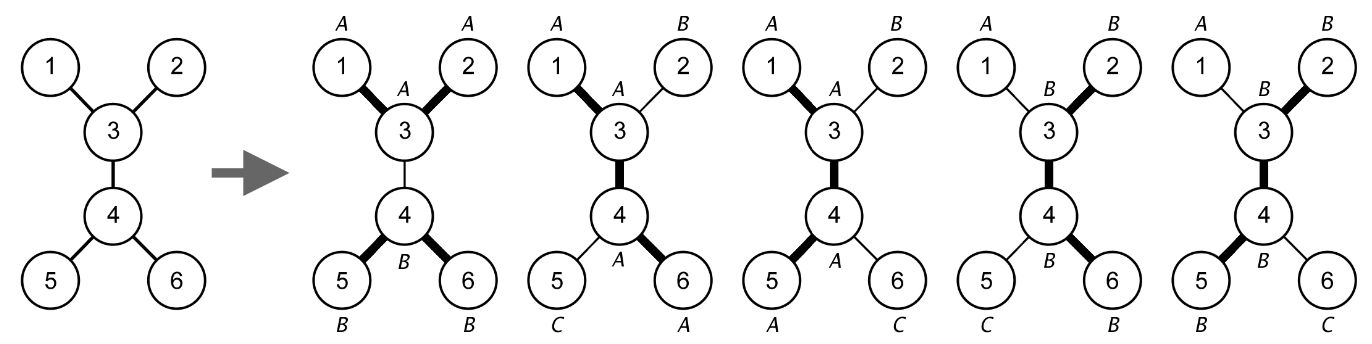
- The first plan uses 2 robots (labeled as A and B in the figure) to clean {1, 2, 3} and {4, 5, 6}.
- The second plan uses 3 robots (labeled as A, B, and C in the figure) to clean {1, 3, 4, 6}, {2}, and {5}.
- The third plan uses 3 robots to clean {1, 3, 4, 5}, {2}, and {6}.
- The fourth plan uses 3 robots to clean {1}, {2, 3, 4, 6}, and {5}.
- The fifth plan uses 3 robots to clean {1}, {2, 3, 4, 5}, and {6}.
No other plans are feasible in this case. For example, the plan {{1, 3}, {2}, {4, 5, 6}} is not feasible as the task {1, 3} and {2} can be combined into a longer path {1, 3, 2}. The plan {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5}, {6}} is also not feasible as {1, 2, 3, 4} is not a path.
Dữ liệu vào
Input begins with a line containing an integer: N (1 \leq N \leq 100 000) representing the number of junctions. The next N - 1 lines each contains two integers: u_i, v_i (1 \leq u_i < v_i \leq N ) representing a road connecting junction u_i and junction v_i. It is guaranteed that it is possible from one junction to go to any other junctions by going through one or more roads.
Dữ liệu ra
Output in a line an integer representing the number of feasible deployment plans. As this output can be large, you need to modulo the output by 1 000 000 007.
Ví dụ
| Dữ liệu vào Sao chép |
6 1 3 2 3 3 4 4 5 4 6 |
| Dữ liệu ra Sao chép |
5 |
| Dữ liệu vào Sao chép |
5 1 2 2 3 2 4 4 5 |
| Dữ liệu ra Sao chép |
3 |